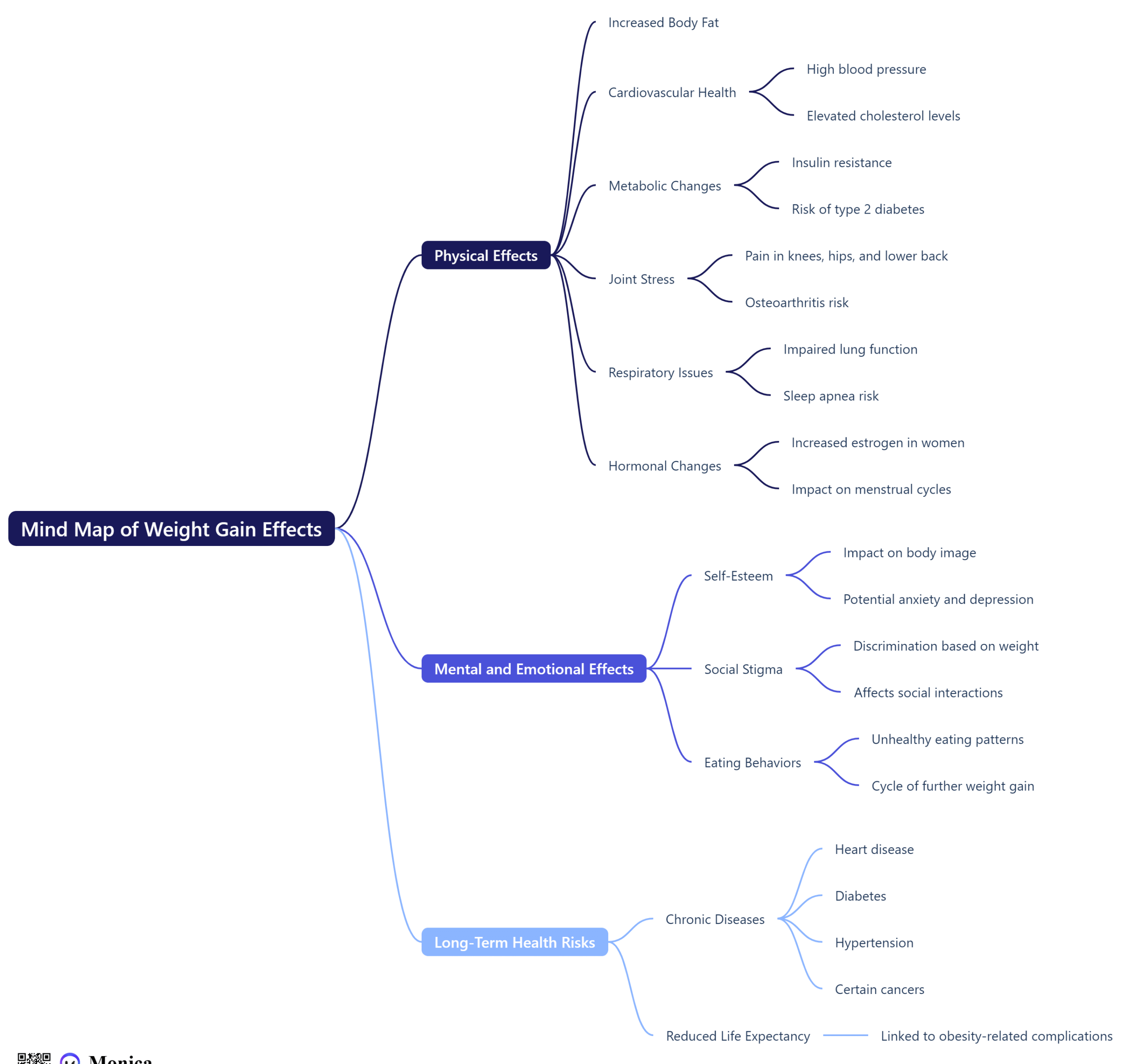
Weight gain can have a variety of effects on the body, both physically and mentally. Here’s a breakdown of the key impacts:
Physical Effects
Increased Body Fat:
Accumulation of excess fat can lead to obesity, which is associated with numerous health issues.
Cardiovascular Health:
Higher body weight can increase blood pressure and cholesterol levels, leading to a greater risk of heart disease and stroke.
Metabolic Changes:
Weight gain can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Joint Stress:
Extra weight places additional stress on joints, particularly in the knees, hips, and lower back, which can lead to pain and conditions like osteoarthritis.
Respiratory Issues:
Excess weight can impair lung function and lead to conditions such as sleep apnea.
Hormonal Changes:
Weight gain can affect hormone levels, including increased estrogen in women, which may influence menstrual cycles and increase the risk of certain cancers.
Mental and Emotional Effects
Self-Esteem:
Weight gain can impact body image and self-esteem, potentially leading to anxiety and depression.
Social Stigma:
Individuals may face stigma or discrimination based on their weight, affecting social interactions and mental health.
Eating Behaviors:
Weight gain can lead to unhealthy eating patterns, which may create a cycle of further weight gain.
Long-Term Health Risks
Chronic Diseases: Increased risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.
Reduced Life Expectancy: Obesity is linked to a shorter lifespan due to associated health complications.
Conclusion
It’s important to approach weight management holistically, considering both physical and mental health. If weight gain is a concern, consulting with healthcare professionals such as doctors or nutritionists can provide personalized strategies for maintaining a healthy weight.